The Arabic alphabet holds a unique and profound significance across various domains, including linguistics, culture, religion, and global communication. As one of the world’s most widely used writing systems, it serves as a cornerstone for understanding not only the Arabic language but also the rich historical and cultural heritage of the Arab world. This article explores the multifaceted importance of the Arabic alphabet, highlighting its historical evolution, cultural impact, and contemporary relevance.
Historical Evolution
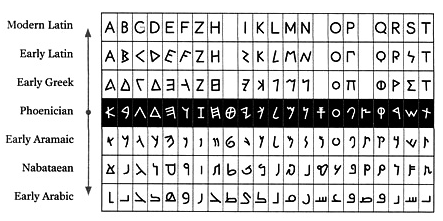
The Arabic alphabet originated from the Nabataean script, which itself evolved from the Aramaic script. Its development began in the early centuries CE, reaching a standardized form by the 7th century. The script was initially used to write Arabic, the language of the Arabian Peninsula, but it soon spread across the Middle East and North Africa with the expansion of Islam. This spread facilitated the alphabet’s adoption for various languages, including Persian, Urdu, and Ottoman Turkish, each of which adapted the script to fit their phonetic needs.
Linguistic Significance
The Arabic alphabet consists of 28 letters and is written from right to left. Its unique features include its cursive nature, where most letters connect to each other within words, and the presence of diacritical marks that indicate short vowels and other phonetic nuances. This cursive style not only distinguishes the Arabic script aesthetically but also influences the way words are read and interpreted. The alphabet’s structure supports a deep connection between spoken and written language, crucial for maintaining linguistic integrity across generations.
Cultural Impact
The Arabic alphabet is more than a tool for communication; it is a vessel for cultural identity and heritage. It is the script of the Quran, the holy book of Islam, making it integral to religious practices and education for millions of Muslims worldwide. The calligraphic art form known as Arabic calligraphy has flourished over centuries, adorning mosques, manuscripts, and various art forms. This calligraphy is not merely decorative but serves as a spiritual and artistic expression of the divine.
Moreover, the script has been instrumental in preserving and transmitting the vast body of Arabic literature, including poetry, philosophy, and science. Classical works by scholars such as Avicenna and Al-Khwarizmi were written in Arabic, significantly contributing to global knowledge and the Renaissance’s intellectual revival.

Contemporary Relevance
In the modern world, the Arabic alphabet continues to be of paramount importance. Arabic is the fifth most spoken language globally, with over 400 million native speakers. It is an official language of the United Nations and serves as a lingua franca in many parts of the Middle East and North Africa. The alphabet’s adaptability has allowed it to remain relevant in the digital age, with Arabic script being widely used on the internet, in social media, and for digital communication.
Additionally, the Arabic script is employed in various modern applications, including typography, graphic design, and advertising. It also plays a crucial role in identity and solidarity among Arabic-speaking communities in the diaspora, preserving cultural ties and heritage.
Conclusion
The Arabic alphabet is a powerful symbol and tool that transcends mere linguistic function. Its historical roots, linguistic features, cultural significance, and contemporary applications underscore its enduring importance. As a bridge between the past and the present, the Arabic alphabet not only fosters communication but also nurtures cultural and religious identity, contributing to the rich tapestry of human civilization.




